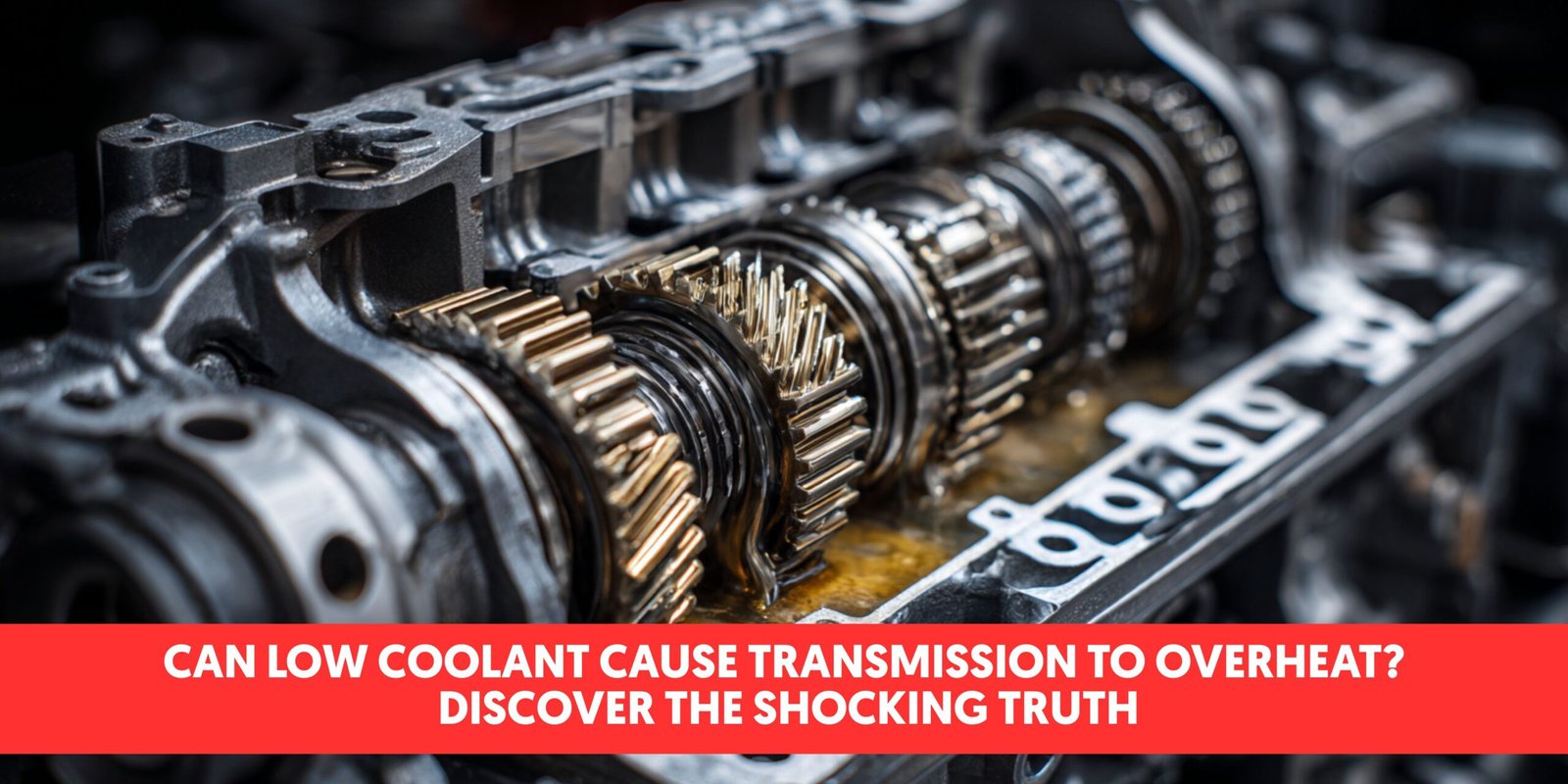
Can low coolant cause your transmission to overheat? If you’ve noticed your vehicle running hotter than usual or experiencing transmission problems, this common culprit might be to blame. The connection between your cooling system and transmission health is stronger than you might think.
Your vehicle relies on proper coolant levels to regulate temperature throughout multiple systems. When coolant runs low, it doesn’t just affect your engine – it can directly impact your transmission too. Many modern vehicles use coolant to help cool transmission fluid through heat exchangers or dedicated cooling lines. Without adequate coolant circulation, transmission fluid temperatures can quickly rise to dangerous levels, potentially leading to costly damage.
Understanding the Relationship Between Coolant and Transmission Temperature
Your vehicle’s cooling system and transmission are interconnected in ways many drivers don’t realize. Coolant doesn’t just regulate engine temperature—it plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal transmission fluid temperatures in many modern vehicles.
How Coolant Affects Transmission Temperature
Coolant circulates through exact transmission cooling systems in many contemporary vehicle models. These systems typically include a transmission cooler integrated into the radiator or as a separate unit. The cooler acts as a heat exchanger, transferring heat from the transmission fluid to the coolant. When coolant levels drop, this heat exchange becomes less efficient, causing transmission fluid to retain more heat.
The Cooling System’s Role in Transmission Health
Modern transmissions operate at temperatures between 175-200°F under normal conditions. Transmission fluid begins to break down at temperatures exceeding 200°F, with severe damage occurring above 240°F. Your vehicle’s cooling system maintains these safe operating temperatures through several key components:
| Component | Function | Impact on Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Radiator | Primary heat exchanger | Contains transmission cooler lines in many vehicles |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant | Ensures proper flow to transmission cooler |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant flow | Controls temperature of coolant reaching transmission |
| Coolant | Heat transfer medium | Directly absorbs heat from transmission fluid |
Transmission coolers rely on proper coolant circulation to dissipate heat effectively. Low coolant levels create a chain reaction: reduced coolant flow leads to higher engine temperatures, which then transfers to the transmission fluid through the shared cooling system infrastructure.
Temperature Interdependence Between Engine and Transmission
Engine and transmission temperatures share a close relationship. An overheating engine inevitably affects transmission temperature through:
- Radiant heat transfer between closely positioned components
- Shared cooling circuits in the radiator system
- Increased operating temperatures throughout the drivetrain
- Compromised efficiency of transmission cooler lines
When coolant levels drop below optimal range, the entire thermal management system becomes compromised. Your transmission absorbs excess heat from both its own operation and the adjacent overheating engine, creating a compounding effect that accelerates fluid breakdown and component wear.
How Engine Coolant Systems Work

Engine coolant systems maintain optimal operating temperatures by circulating a mixture of water and antifreeze through your vehicle’s engine. This circulation process effectively removes excess heat from the engine components and transfers it to the surrounding air through the radiator.
The Role of Coolant in Heat Management
Coolant does more than just regulate engine temperature—it’s instrumental in managing transmission heat as well. The antifreeze mixture absorbs heat from both the engine block and transmission fluid as it flows through the system. Heat transfer occurs when hot transmission fluid passes through a dedicated cooler that’s typically integrated with the radiator. Your vehicle’s cooling system creates a thermal equilibrium by allowing the cooler coolant to absorb heat from the hotter transmission fluid, then releasing that heat through the radiator fins. Without adequate coolant levels, this critical heat exchange becomes compromised, forcing your transmission to operate at higher temperatures than designed.
Transmission Cooling Mechanisms
Transmission cooling relies on a specialized heat exchange system that works alongside your engine’s cooling circuit. Modern vehicles incorporate transmission coolers—usually mounted within the radiator assembly—where hot transmission fluid passes through small tubes surrounded by engine coolant. The temperature differential between these fluids enables efficient heat transfer from the transmission to the coolant. Your transmission fluid circulates continuously between the transmission and this cooler, shedding heat with each cycle. External coolers may supplement this system in vehicles designed for heavy-duty applications like towing or hauling. Cooling efficiency drops dramatically with low coolant levels because there’s insufficient liquid to absorb and dissipate the transmission’s heat load, creating a dangerous condition where transmission components expand, internal pressure increases, and seals may fail. This inefficient cooling accelerates fluid breakdown, reducing its lubricating properties and eventually leading to increased friction and component wear throughout the transmission system.
Can Low Coolant Cause Transmission Overheating?

Low coolant can indirectly cause transmission overheating because most modern vehicles use integrated cooling systems where the transmission relies on the engine’s cooling capacity. This connection means coolant issues affect both engine and transmission temperatures simultaneously.
Direct Impact on Transmission Coolers
Transmission coolers depend on proper coolant levels for effective heat exchange with transmission fluid. These coolers, typically integrated with or positioned near the radiator, remove excess heat from transmission fluid through thermal exchange with engine coolant. When coolant levels drop, the radiator’s efficiency decreases substantially, compromising its ability to cool transmission fluid passing through the cooler. This reduced cooling capacity forces transmission fluid to retain more heat, causing temperature spikes that can reach damaging levels. The interconnected nature of these systems means that coolant problems quickly translate to transmission cooling issues, even when transmission fluid levels remain normal.
Indirect Effects Through Engine Overheating
Engine overheating from low coolant creates additional thermal stress on transmission components. As engine temperatures rise due to insufficient coolant, the entire underhood environment becomes hotter, exposing transmission components to excessive ambient heat. This elevated temperature environment impairs the transmission’s ability to dissipate heat through normal means. Besides, engine overheating often affects critical cooling system components like radiator fans and thermostats, which play essential roles in transmission cooling. The compromised operation of these components creates a compounding effect where transmission temperatures continue climbing beyond safe operating ranges of 175-200°F. While transmission problems are more commonly associated with low transmission fluid or clogged coolers, low coolant represents a important contributing factor that shouldn’t be overlooked during diagnosis of transmission overheating issues.
Warning Signs of Low Coolant Affecting Your Transmission

Recognizing the early signs of low coolant impacting your transmission can save you from costly repairs. Your vehicle communicates these issues through various warning indicators and performance changes that shouldn’t be ignored.
Dashboard Warning Indicators
Your dashboard serves as the first line of defense against transmission problems related to low coolant. The transmission temperature warning light illuminates when your transmission fluid exceeds safe operating temperatures, often resulting from insufficient cooling. Your check engine light may also activate, indicating potential cooling system issues that affect both engine and transmission performance. The coolant temperature warning light specifically alerts you to dangerous engine temperatures, which directly impact transmission cooling efficiency. These dashboard warnings function as an early alert system, giving you time to address cooling problems before severe transmission damage occurs.
Performance Symptoms
Your vehicle’s performance noticeably changes when low coolant begins affecting transmission function. A distinct burning odor, often sweet-smelling or charred, indicates overheated transmission fluid and requires immediate attention. Your transmission may exhibit slipping gears or delayed shifting responses as fluid properties deteriorate from excessive heat. Driving becomes increasingly difficult when your vehicle hesitates, grinds, or shakes during acceleration or while idling at stoplights. Your temperature gauge climbing into the red zone signals insufficient coolant that compromises both engine and transmission cooling systems simultaneously. Unusual noises during gear changes often accompany these symptoms, further confirming the relationship between cooling system problems and transmission performance.
Preventing Transmission Damage from Coolant Issues

Proper maintenance of your vehicle’s cooling system is essential for protecting your transmission from heat-related damage. Low coolant levels directly impact transmission temperatures, potentially leading to costly repairs and component failures if left unaddressed.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Regular coolant system checks form the cornerstone of transmission protection. Monitor your coolant levels at least monthly, inspecting the reservoir to ensure it’s between the minimum and maximum markings. Coolant lines require periodic examination for signs of wear, cracks, or damage that might cause leaks and subsequent transmission overheating. Establishing a consistent maintenance routine helps identify potential issues before they escalate into major transmission problems. Following your vehicle manufacturer’s recommended service intervals for coolant replacement ensures the fluid maintains its heat transfer properties, typically every 30,000 to 50,000 miles depending on your exact vehicle model.
Proper Coolant Selection and Levels
Using the correct coolant type dramatically affects your transmission’s thermal regulation capabilities. Different vehicles require exact coolant formulations—some need extended-life variants while others perform best with conventional antifreeze. Consulting your owner’s manual provides definitive guidance on the appropriate coolant for your vehicle’s cooling system. Maintaining proper coolant concentration (typically a 50/50 mix with distilled water) optimizes the system’s heat transfer efficiency. Insufficient coolant levels prevent adequate circulation through transmission cooling components, while contaminated or degraded coolant can’t effectively absorb heat from transmission fluid. Topping off coolant when it falls below recommended levels and performing complete flushes according to maintenance schedules ensures your transmission receives consistent cooling protection during operation.
How to Check and Maintain Proper Coolant Levels

Checking your vehicle’s coolant levels regularly prevents both engine and transmission overheating issues. The coolant reservoir is typically a translucent plastic tank located near the radiator with clearly marked “Min” and “Max” level indicators. When examining coolant levels, always ensure the engine is completely cold to avoid burns from hot fluid or steam.
Regular inspection involves looking under your vehicle for any coolant leaks, which appear as green, orange, or pink puddles depending on the coolant type. Coolant levels should consistently remain between the minimum and maximum marks on the reservoir. Addressing low levels promptly helps maintain efficient heat transfer throughout your vehicle’s cooling system.
When refilling coolant, use only the exact type recommended in your owner’s manual to ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s cooling system components. Mixing different coolant types can reduce cooling efficiency and potentially damage internal components. Monthly coolant checks are ideal for preventive maintenance, with additional inspections recommended before embarking on long trips.
Following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for complete coolant flushes keeps the cooling system operating at peak efficiency. Most vehicles require coolant replacement every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, though this varies by model and driving conditions. Proper coolant maintenance not only protects your engine but also safeguards your transmission from indirect heat damage caused by cooling system inefficiencies.
Long-Term Consequences of Transmission Overheating
Transmission fluid deterioration occurs rapidly when your transmission overheats due to low coolant levels. This fluid breakdown significantly reduces its lubricating properties, creating excessive friction between moving parts and accelerating wear on critical transmission components. Heat-damaged fluid can’t properly protect your transmission’s internal mechanisms, leading to a cascade of increasingly serious problems.
Seals and gaskets crack under prolonged exposure to excessive heat, resulting in fluid leaks that further deplete your transmission’s protection. These compromised seals allow transmission fluid to escape while potentially letting contaminants enter the system. Clutches and bands within your transmission begin to slip when overheated, causing erratic performance and accelerating internal damage to friction surfaces.
Gear systems suffer permanent damage when transmission temperatures remain too high for extended periods. Metal components can warp, leading to improper meshing of gear teeth and eventual mechanical failure. Transmission bearings lose their precision tolerances when subjected to extreme heat, creating additional friction points and noise during operation.
Shifting performance degrades noticeably as your transmission continues to overheat. You’ll experience delayed engagement when shifting from park to drive, harsh or slipping gear changes during acceleration, and potentially dangerous unpredictable behavior in traffic situations. These symptoms indicate serious internal damage is already occurring within your transmission.
The financial impact of transmission overheating proves substantial in most cases. Repair costs for heat-damaged transmissions typically range from $2,000 to $4,000 depending on vehicle make and model. Complete transmission replacement becomes necessary in severe cases, potentially doubling these expenses when labor and additional components are factored into the repair bill.
Vehicle reliability diminishes dramatically once transmission overheating has caused important internal damage. Your transmission may fail completely without warning, leaving you stranded and facing not only repair costs but additional expenses for towing and alternative transportation. Resale value drops substantially when a vehicle has transmission damage in its history, further compounding the financial consequences.
Conclusion
Low coolant absolutely can cause your transmission to overheat. The interconnected nature of modern vehicle cooling systems means that coolant issues affect both your engine and transmission simultaneously.
Maintaining proper coolant levels isn’t just an engine concern – it’s essential for transmission health too. Regular checks take just minutes but can save you thousands in potential repair costs.
Remember that heat is your transmission’s worst enemy. By monitoring coolant levels being alert to warning signs and following manufacturer maintenance schedules you’re protecting both systems from premature failure.
Don’t wait until you notice performance issues. A proactive approach to coolant maintenance will keep your transmission running cooler longer and extend the life of your vehicle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can low coolant really affect my transmission?
Yes, low coolant can significantly impact your transmission. Modern vehicles use coolant to regulate transmission fluid temperature through specialized cooling systems. When coolant levels are low, the transmission fluid can’t cool properly, causing it to overheat. This overheating accelerates fluid breakdown and component wear, potentially leading to expensive transmission damage.
What temperature should my transmission normally operate at?
Most modern transmissions are designed to operate safely between 175-200°F (79-93°C). At these temperatures, the transmission fluid provides optimal lubrication and hydraulic pressure. When temperatures exceed 200°F, transmission fluid begins to break down rapidly. Above 240°F, serious damage can occur within minutes, significantly reducing transmission lifespan.
What are the warning signs of transmission overheating?
Look for dashboard warning lights (temperature or transmission warnings), burning odors (similar to burning paper), slipping gears or delayed engagement, unusual transmission noises, and fluid leaks under your vehicle. Your vehicle may also go into “limp mode” with limited performance to protect components from further damage. Address these symptoms immediately to prevent costly repairs.
How often should I check my coolant levels?
Check your coolant levels monthly as part of routine maintenance, and always before long trips. The coolant reservoir is typically a translucent plastic tank with “Min” and “Max” indicators. Check when the engine is cold, and inspect for leaks under the vehicle. Follow your manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for complete coolant flushes, typically every 30,000-50,000 miles.
What happens if I ignore transmission overheating?
Ignoring transmission overheating leads to rapid fluid deterioration, reduced lubrication, and increased friction between moving parts. This causes cracked seals and gaskets, fluid leaks, and slipping clutches. Eventually, metal components warp, shifting performance degrades, and complete mechanical failure occurs. Repair costs typically range from $2,000-$4,000, with potential for complete transmission replacement.
Can I just add any coolant to my vehicle?
No, you should only use the coolant type recommended in your owner’s manual. Different vehicles require specific coolant formulations that are compatible with their cooling system materials. Using the wrong coolant can cause corrosion, scaling, or other damage to your cooling system and potentially void your warranty. If you’re unsure, consult your vehicle manufacturer or a qualified mechanic.
How are engine cooling and transmission cooling connected?
Most modern vehicles have integrated cooling systems where the transmission relies on the engine’s cooling capacity. The coolant circulates through the engine and then through a transmission cooler (typically located within the radiator) that acts as a heat exchanger. This system transfers heat from the transmission fluid to the coolant. When coolant levels are low, both engine and transmission temperatures rise simultaneously.
How expensive are transmission repairs caused by overheating?
Transmission repairs due to overheating are costly, typically ranging from $2,000 to $4,000 depending on vehicle make and model. Complete transmission replacement can exceed $5,000 for some vehicles. These expenses far outweigh the simple cost of maintaining proper coolant levels and following recommended maintenance schedules, making prevention the most economical approach.
Related Posts: