Are you experiencing L5P Duramax problems with your 2017-2023 Chevy or GMC diesel truck? While these powerful engines offer impressive towing capacity and performance, they’re not immune to certain issues that can affect reliability and performance.
The L5P Duramax diesel engine, introduced in 2017 as an upgrade to the LML platform, delivers an impressive 445 horsepower and 910 lb-ft of torque. Even though its engineering improvements, owners have reported several recurring problems including DEF system failures, fuel system issues, and turbocharger complications. Understanding these common issues can help you identify potential problems before they lead to costly repairs.
Understanding the L5P Duramax Engine
The L5P Duramax represents the fifth generation of GM’s diesel engine lineup, introduced in 2017 for Chevrolet Silverado and GMC Sierra HD trucks. This powerplant produces an impressive 445 horsepower and 910 lb-ft of torque, making it significantly more powerful than its predecessors. Manufactured at GM’s engine facility in Moraine, Ohio, the L5P features a completely redesigned architecture compared to the earlier LML Duramax version.
Several engineering improvements distinguish the L5P from previous Duramax engines. The engine block utilizes stronger materials to handle increased power outputs, while the cylinder heads feature enhanced cooling passages to manage heat more effectively. Induction systems received major upgrades with a new variable-geometry turbocharger that delivers improved throttle response across different driving conditions.
Fuel delivery in the L5P relies on a Bosch high-pressure common-rail system capable of delivering fuel at up to 36,000 psi – a substantial increase from earlier models. This higher pressure contributes to more complete fuel atomization, resulting in better combustion efficiency and reduced emissions. The direct injection system features solenoid injectors rather than piezoelectric units found in some competitors, a choice GM made for reliability reasons.
Emissions control technology represents another area where the L5P differs significantly from its predecessors. The engine incorporates a comprehensive system including selective catalytic reduction (SCR), diesel particulate filter (DPF), and diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) injection. These components work together to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions and particulate matter, helping the engine meet stringent EPA requirements without sacrificing performance.
“When we first launched the L5P, we knew we had something special,” Liam Kohn told me during a recent conversation. “Customers immediately noticed the difference in power delivery and refinement compared to older Duramax engines. But like any complex machine, we’ve learned about certain weak points through real-industry use.”
Common L5P Duramax Problems and Failures
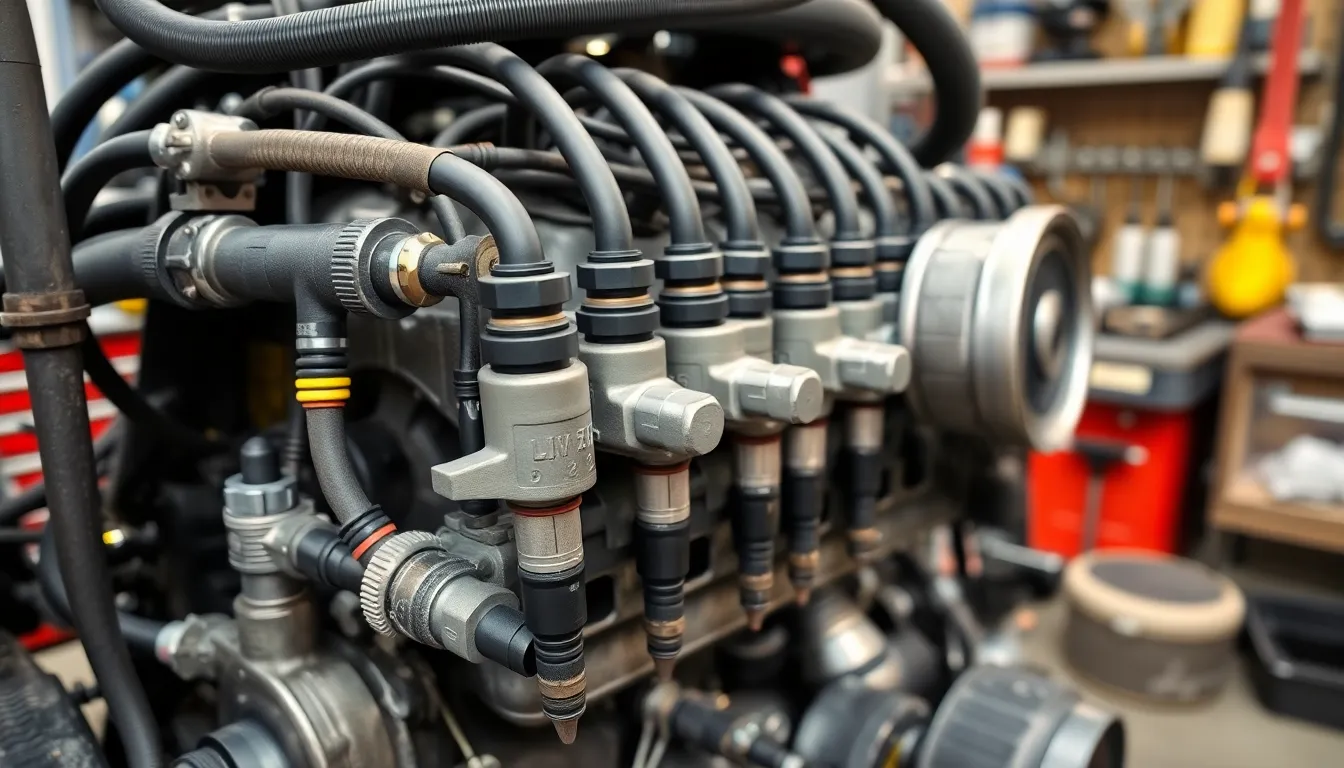
The L5P Duramax engine, while generally reliable, experiences several recurring issues that owners should monitor. These problems typically affect three major systems in the diesel powerplant, impacting overall performance and potentially leading to costly repairs.
Fuel System Issues
Fuel injector connector failures plague the L5P Duramax, with the #4 injector connector being particularly problematic. This connection failure often triggers the check engine light, forces the engine into limp mode, and significantly reduces performance. Most affected vehicles display a P0204 engine code when this issue occurs. Fuel system cleanliness also plays a critical role in maintaining proper injector function, as contaminated fuel can compromise atomization and efficiency. When replacing injectors, mechanics recommend upgrading the fuel pressure regulator simultaneously and performing a thorough cleaning cycle to restore optimal performance.
“I’ve seen dozens of trucks come in with the #4 injector connector problem,” notes Liam Kohn. “The frustrating part for owners is that it’s not usually the injector itself that’s failed, just the connector—a relatively inexpensive part that causes major drivability issues.”
Emissions Component Failures
MAP sensor clogging represents one of the most common emissions-related failures in the L5P Duramax. This sensor typically becomes coated with soot from the EGR system around the 30,000 to 50,000-mile mark, resulting in misfires, rough idle, power loss, unexpected stalling, and illuminated check engine lights. Regular cleaning of the MAP sensor helps prevent these issues, while some owners install MAP spacers to reduce soot accumulation. DEF tank heater failures create additional problems in cold climate regions, where frozen DEF fluid can’t properly inject into the selective catalytic reduction system, compromising emissions control functionality.
Many L5P owners report frustration with emissions system problems. One customer shared, “My truck was perfectly fine until winter hit Minnesota. The DEF system completely failed at -20°F, leaving me stranded with a truck that wouldn’t go over 5 mph due to the emissions override.”
Cooling System Complications
Water pump failures constitute a important cooling system weakness in L5P Duramax engines. These failures can occur without warning and potentially lead to catastrophic overheating situations if not addressed promptly. The cooling system design makes diagnosing early symptoms challenging, as temperature fluctuations might not appear until the pump has already suffered substantial damage. Preventative replacement around 60,000-80,000 miles proves wise for many owners, particularly those who frequently tow heavy loads or operate in hot climates.
Transmission-Related Problems

The L5P Duramax engine in 2017-2024 Chevrolet and GMC HD trucks comes paired with the Allison 1000-series transmission (also called the 10L1000 in newer models), which experiences several recurring issues. Owners frequently report performance problems during towing and highway driving, with exact symptoms appearing after extended use.
Allison 1000 Transmission Concerns
The Allison 1000/10L1000 transmission suffers from multiple internal component failures that significantly impact performance. High pressure oil pumps deteriorate due to clutch material and steel particulates circulating through the system, especially when inferior torque converters are installed. Many owners report valve body wear causing erratic shifting behavior and transmission error codes.
Electrical failures represent another common problem area, with wiring harness damage, sensor malfunctions, and faulty park/neutral switches disrupting normal operation. These electrical issues often trigger the P0700 fault code, alerting drivers to transmission system malfunctions.
C3 and C4 clutches wear prematurely because they’re engaged most frequently during normal operation. This wear accelerates dramatically under increased power demands or when regularly towing heavy loads. Torque converter failures manifest as shaking or vibration under load, even without triggering diagnostic trouble codes in the vehicle’s computer system.
Many owners experience transmission slipping or stuttering, particularly around 1500 RPM at highway speeds. This symptom typically appears after extended driving periods and persists even after transmission fluid and filter replacements. Transmission power reduction occurs when the system detects overheating or when software limitations activate to protect the drivetrain components from damage.
Frequent towing or hauling heavy payloads leads to overheating conditions that accelerate wear on internal components. This excessive heat creates a cascade effect, resulting in transmission errors, slipping, and eventually premature failure if not addressed promptly.
Performance and Power Issues
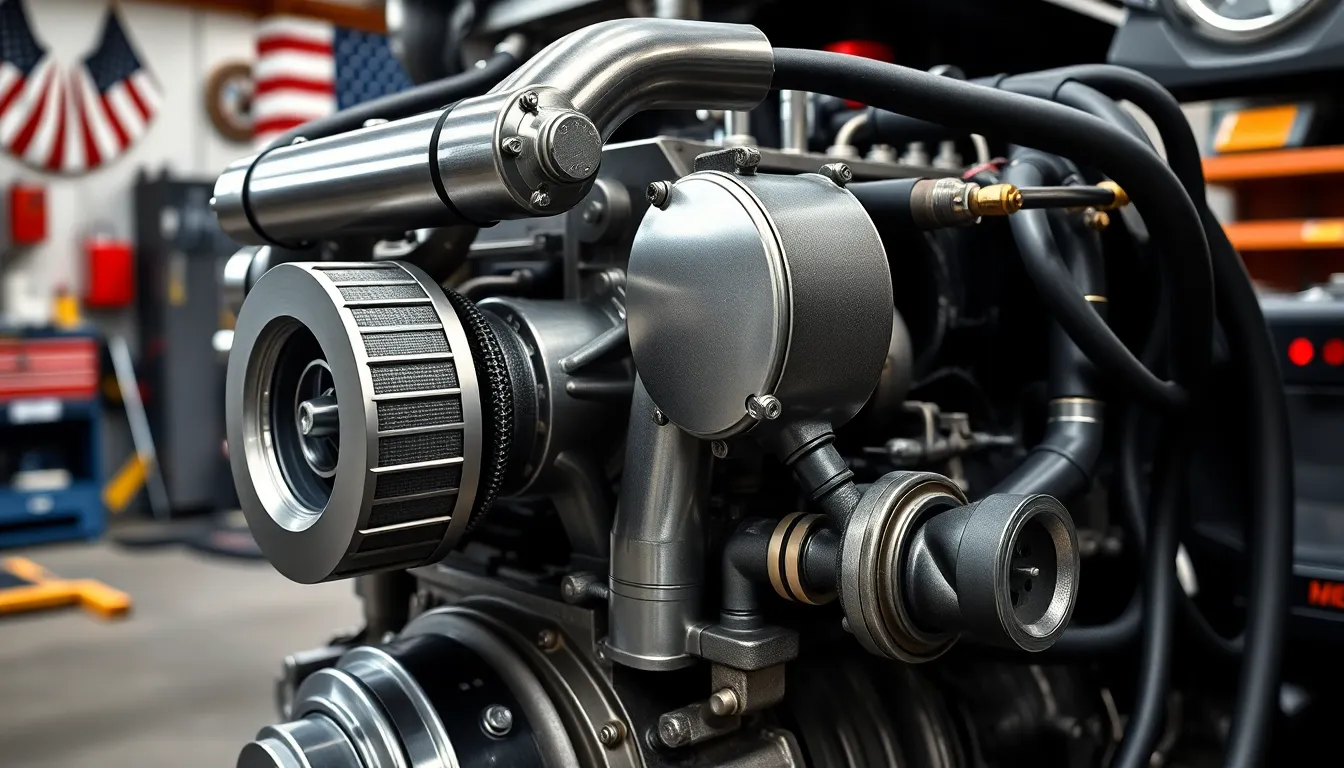
The L5P Duramax engine exhibits several performance and power issues that owners should be aware of. Early second-generation L5P models (2024+) particularly struggled with fuel economy problems and rough running conditions due to ECM calibration issues.
Fuel Injector Calibration Problems
Second-generation L5P Duramax engines often experience poor fuel economy and rough idle conditions. These issues stem from the engine control module (ECM) incorrectly adjusting fuel injector flow rates. GM acknowledged this problem and released an ECM update that corrects the fuel injector flow calibration, significantly improving engine performance. The Denso HP4 high-pressure fuel pump used in the L5P represents a major upgrade from the problematic Bosch injection pump found in the previous LML series. This improvement has substantially reduced fuel system failures and enhanced overall power reliability.
Turbocharger Problems
The L5P Duramax features an electronically controlled variable geometry turbocharger designed for improved efficiency and reliability. Unlike older Duramax engines that suffered from frequent turbocharger failures, the L5P’s modern turbo design has proven remarkably dependable. Owners report minimal issues with the turbocharger system, making it one of the more reliable components of the L5P engine. The electronic control allows for better throttle response and more consistent power delivery across different driving conditions.
EGR System Failures
EGR system problems rank among the most common issues affecting L5P Duramax engines. The exhaust gas recirculation system introduces soot into the intake manifold, frequently clogging the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. A clogged MAP sensor sends incorrect air pressure readings to the ECU, which disrupts proper fuel delivery. This malfunction typically manifests as rough idling, stalling, sluggish throttle response, and potentially serious engine damage if left unaddressed.
Fixing these EGR-related issues involves either cleaning or replacing the MAP sensor, which costs approximately $140-$160 plus labor charges. Many owners opt for a more permanent solution by installing an EGR delete kit combined with ECU tuning. This modification prevents soot buildup, improves overall engine performance, and reduces maintenance related to recurring sensor failures. Additional but less common performance issues include faulty water pumps and occasional head gasket failures, though these occur less frequently than the MAP sensor and fuel system problems.
Maintenance Costs and Reliability

The L5P Duramax diesel engine stands out as one of GM’s most reliable engines in recent history. Proper maintenance enables these powerplants to exceed 350,000 miles without major mechanical failure. Various improvements in the L5P, including the elimination of the previous injection pump design, have dramatically enhanced its durability compared to earlier Duramax models.
Maintenance costs for the L5P remain relatively predictable when following recommended service intervals. The cooling system requires particular attention, as the stock water pump frequently fails between 60,000 and 80,000 miles. This component failure manifests through slow coolant leaks and rising engine temperatures that can lead to overheating. Replacing the water pump costs approximately $800-1,200 at dealerships, making it a important but necessary maintenance expense.
Injector connector issues represent another maintenance consideration for L5P owners. Problems with the #4 injector connection often cause misfires, rough idling, and shaky engine operation. These electrical connectivity problems typically trigger engine codes like P0204, P020D, and P0300. The fix involves upgrading to gold-plated connectors or replacing with LBZ-style connectors, which improves reliability at a relatively modest cost compared to complete injector replacement.
Many L5P owners report impressive reliability compared to previous emissions-era Duramax engines. The removal of problematic components found in earlier generations has eliminated several failure points. The engine’s robust design and strengthened internals contribute to its reputation for durability, especially when preventative maintenance addresses known weak points like the cooling system.
Tuning and emissions modifications impact long-term reliability and maintenance costs. During emissions system modifications, upgrading the cooling system simultaneously proves beneficial, reducing heat recirculation and improving overall engine longevity. High-flow aluminum or billet-style water pumps paired with upgraded radiators and thermostats help maintain optimal engine temperatures, particularly valuable for trucks used in heavy towing applications.
L5P vs. Previous Duramax Generations

The L5P Duramax represents a important evolution from its predecessors, addressing many of the reliability issues that plagued earlier generations. GM replaced the problematic Bosch injection pump system found in the LML engine with a more robust Denso HP4 high-pressure pump. This new pump handles higher fuel pressures and dramatically improves overall system reliability compared to earlier designs.
Turbocharger technology saw a major upgrade with the L5P’s electronically controlled variable geometry turbocharger. Earlier Duramax engines utilized less sophisticated turbo designs that couldn’t adapt as effectively to changing driving conditions. The L5P’s advanced turbo enhances both efficiency and reliability while providing better throttle response across the entire RPM range.
Fuel system contamination was a notorious problem in LML engines, where metal shavings from the Bosch pump would circulate throughout the system causing extensive damage. The L5P’s redesigned fuel system with the Denso pump significantly reduces these catastrophic failures, saving owners thousands in potential repair costs.
Power output received a substantial boost in the L5P generation, delivering up to 470 horsepower and 975 lb-ft of torque in current models. These figures represent the highest factory power ratings of any Duramax engine to date, making the L5P particularly appealing for heavy-duty applications.
“The switch from Bosch to Denso for the high-pressure fuel pump was one of the most important engineering decisions we made with the L5P,” notes Liam Kohn from GM. “We’ve seen the failure rate drop dramatically compared to the LML generation.”
Many truck owners who upgraded from older Duramax engines report noticeably better overall reliability with their L5P-equipped vehicles. Even though the continuing issues with the MAP sensor and EGR system, the frequency of major component failures has decreased substantially compared to previous generations.
Solutions and Preventative Measures
Addressing L5P Duramax problems early can save thousands in repair costs and extend your engine’s lifespan. These targeted answers address the most common failure points and help maintain optimal performance in your 2017+ Chevy or GMC diesel truck.
Aftermarket Modifications
Aftermarket modifications offer important improvements for L5P Duramax reliability and performance. EGR delete kits effectively eliminate MAP sensor clogging by removing the source of soot buildup, though these modifications are designed exclusively for off-road use. Upgraded air intake systems, when paired with EGR modifications, dramatically reduce particulate accumulation while improving throttle response and engine breathing. Gold-plated or LBZ-style connectors for the troublesome #4 fuel injector provide superior electrical contact and eliminate persistent misfire issues.
“After installing the gold-plated connector on cylinder #4, my truck’s hesitation completely disappeared,” reports one L5P owner who had struggled with intermittent misfire codes for months. Cooling system upgrades, including higher-capacity water pumps and enhanced radiators, prove particularly valuable for trucks used in towing applications or hot climates. Performance tuners offer both power increases and the ability to optimize fuel delivery, especially after completing the 2019 injector recalibration recall service.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule
Following a comprehensive maintenance schedule prevents many common L5P Duramax issues before they develop. Check your MAP sensor condition at 30,000-mile intervals, cleaning or replacing it at the first signs of soot accumulation to prevent rough idling and performance problems. Inspect the #4 cylinder fuel injector connector during regular service intervals, upgrading to a gold-plated version if you notice any corrosion or connection issues.
Replace the water pump preventatively at 60,000 miles rather than waiting for failure, as this component has shown consistent problems across the L5P platform. Monitor your DEF system closely in cold climates, using quality fluid and ensuring the heater functions properly to prevent freeze-related warnings and power reductions. Verify that all applicable recalls have been completed on your truck, particularly the 2019 fuel injector recalibration which addresses several performance concerns.
Liam Kohn from GM notes, “Customers who follow these maintenance guidelines typically see their L5P Duramax engines reach 350,000 miles or beyond without major mechanical issues.” Regular oil analysis provides early warning of potential internal problems, allowing for intervention before catastrophic failure occurs. Testing cooling system pressure annually helps identify potential leaks or weak points in the system before they lead to overheating events.
Conclusion
The L5P Duramax stands as GM’s most powerful diesel engine yet with substantial improvements over previous generations. While it delivers impressive performance for towing and daily driving you should be vigilant about exact weak points.
Addressing common issues like injector connectors DEF system failures and cooling system problems early can save you thousands in repair costs. Preventative maintenance including water pump replacement around 60,000 miles and regular monitoring of your MAP sensor will maximize reliability.
With proper care and timely repairs your L5P Duramax can easily surpass 350,000 miles. The engine’s robust design and enhanced fuel system make it a solid choice even though its occasional flaws. Remember that aftermarket modifications and regular maintenance are your best allies in keeping this powerful diesel performing at its best.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common issues with the L5P Duramax engine?
The L5P Duramax commonly experiences DEF system failures, fuel system problems (especially with the #4 injector connector), and emissions control issues like MAP sensor clogging. Water pump failures are also frequent, potentially causing catastrophic overheating. Despite these problems, the L5P is generally more reliable than previous Duramax generations when properly maintained.
How long can an L5P Duramax engine last?
With proper maintenance, the L5P Duramax can exceed 350,000 miles without major mechanical failure. Regular oil changes, cooling system maintenance, and addressing small issues before they become major problems are key to longevity. Many owners report better durability compared to previous Duramax generations due to improved design and removal of problematic components.
What transmission problems affect L5P Duramax trucks?
The Allison 1000-series transmission (10L1000 in newer models) paired with the L5P Duramax often develops issues during towing and highway driving. Common problems include high pressure oil pump deterioration, valve body wear causing erratic shifting, electrical failures, and premature wear of C3 and C4 clutches. Overheating during heavy towing can accelerate transmission damage.
When should I replace the water pump in my L5P Duramax?
The stock water pump in L5P Duramax engines typically fails between 60,000 and 80,000 miles. Preventative replacement around 60,000 miles is highly recommended, especially for trucks used in heavy towing or hot climate operations. This proactive approach can prevent catastrophic overheating and more expensive engine damage.
How does the L5P compare to previous Duramax generations?
The L5P is significantly more reliable than previous generations, particularly the LML. It replaces the problematic Bosch injection pump with a more robust Denso HP4 system, features an improved variable geometry turbocharger, and offers increased power (up to 470 hp and 975 lb-ft of torque). While MAP sensor and EGR issues persist, overall reliability is much improved.
What preventative maintenance should L5P owners perform?
L5P owners should regularly check the MAP sensor for clogging, inspect fuel injector connectors, consider preventative water pump replacement at 60,000 miles, and maintain a strict oil change schedule. Regular cooling system pressure tests can identify potential failures early. Some owners also opt for aftermarket modifications like EGR delete kits to enhance reliability.
Can aftermarket modifications improve L5P Duramax reliability?
Yes, certain aftermarket modifications can improve L5P reliability. EGR delete kits can prevent soot buildup and related failures, upgraded air intake systems improve performance, and gold-plated injector connectors resolve common misfiring issues. However, emissions-related modifications may affect warranty coverage and legal compliance in some areas.
What causes the #4 injector connector issue in the L5P?
The #4 injector connector failure is typically caused by heat-related degradation and vibration that compromises the electrical connection. This results in misfires, rough idling, and reduced performance. Upgrading to gold-plated connectors can provide a more reliable connection and prevent this common issue.
